RNN 循环神经网络 (回归)
学习资料:
要点 ¶
循环神经网络让神经网络有了记忆, 对于序列话的数据,循环神经网络能达到更好的效果. 如果你对循环神经网络还没有特别了解, 请观看几分钟的短动画, RNN 动画简介 和 LSTM 动画简介 能让你生动理解 RNN. 上次我们提到了用 RNN 的最后一个时间点输出来判断之前看到的图片属于哪一类, 这次我们来真的了, 用 RNN 来及时预测时间序列.
训练数据 ¶
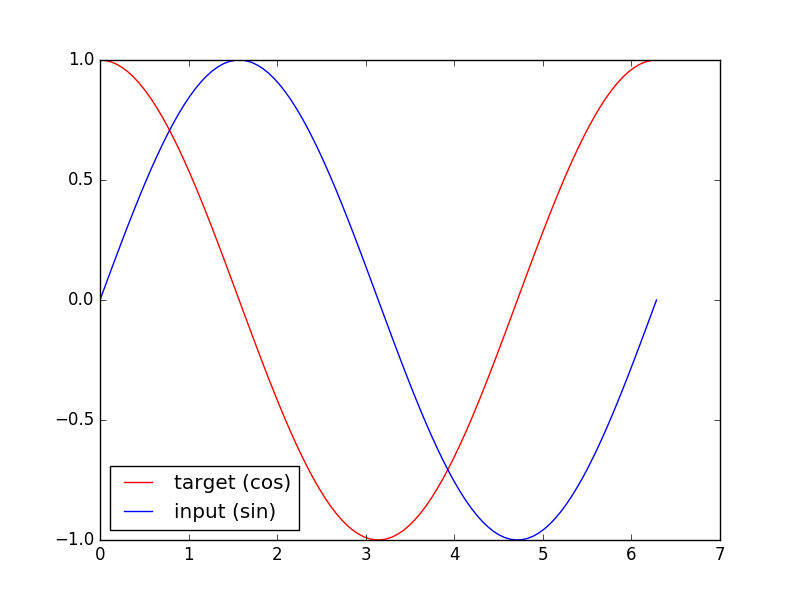
我们要用到的数据就是这样的一些数据, 我们想要用 sin 的曲线预测出 cos 的曲线.
import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# Hyper Parameters
TIME_STEP = 10 # rnn time step / image height
INPUT_SIZE = 1 # rnn input size / image width
LR = 0.02 # learning rate
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False # set to True if haven't download the data
RNN模型 ¶
这一次的 RNN, 我们对每一个 r_out 都得放到 Linear 中去计算出预测的 output, 所以我们能用一个 for loop 来循环计算.
这点是 Tensorflow 望尘莫及的! 除了这点, 还有一些动态的过程都可以在这个教程中查看, 看看我们的 PyTorch 和 Tensorflow 到底哪家强.
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.RNN( # 这回一个普通的 RNN 就能胜任
input_size=1,
hidden_size=32, # rnn hidden unit
num_layers=1, # 有几层 RNN layers
batch_first=True, # input & output 会是以 batch size 为第一维度的特征集 e.g. (batch, time_step, input_size)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32, 1)
def forward(self, x, h_state): # 因为 hidden state 是连续的, 所以我们要一直传递这一个 state
# x (batch, time_step, input_size)
# h_state (n_layers, batch, hidden_size)
# r_out (batch, time_step, output_size)
r_out, h_state = self.rnn(x, h_state) # h_state 也要作为 RNN 的一个输入
outs = [] # 保存所有时间点的预测值
for time_step in range(r_out.size(1)): # 对每一个时间点计算 output
outs.append(self.out(r_out[:, time_step, :]))
return torch.stack(outs, dim=1), h_state
rnn = RNN()
print(rnn)
"""
RNN (
(rnn): RNN(1, 32, batch_first=True)
(out): Linear (32 -> 1)
)
"""
其实熟悉 RNN 的朋友应该知道, forward 过程中的对每个时间点求输出还有一招使得计算量比较小的.
不过上面的内容主要是为了呈现 PyTorch 在动态构图上的优势,
所以我用了一个 for loop 来搭建那套输出系统. 下面介绍一个替换方式. 使用 reshape 的方式整批计算.
def forward(self, x, h_state):
r_out, h_state = self.rnn(x, h_state)
r_out_reshaped = r_out.view(-1, HIDDEN_SIZE) # to 2D data
outs = self.linear_layer(r_out_reshaped)
outs = outs.view(-1, TIME_STEP, INPUT_SIZE) # to 3D data
训练 ¶
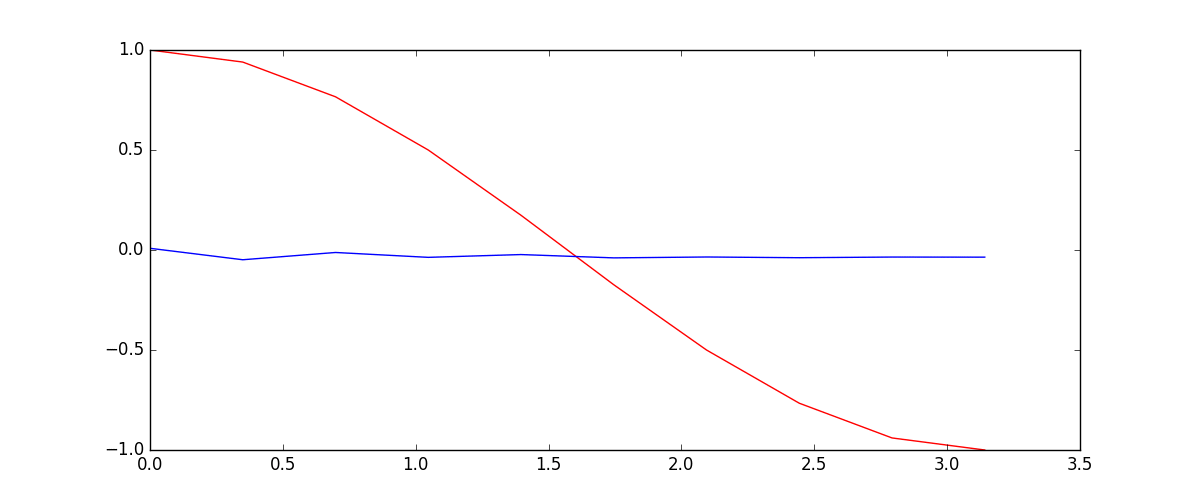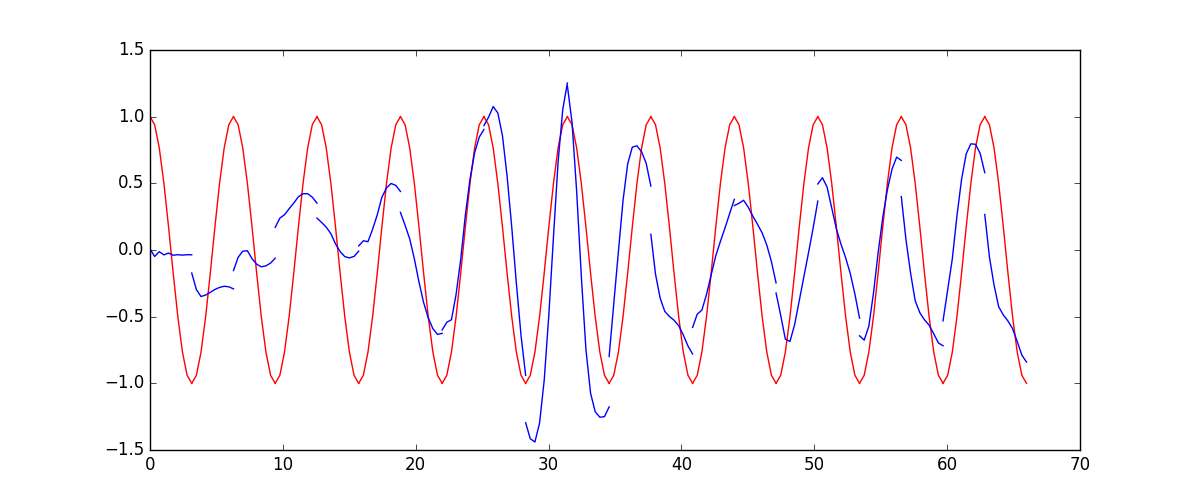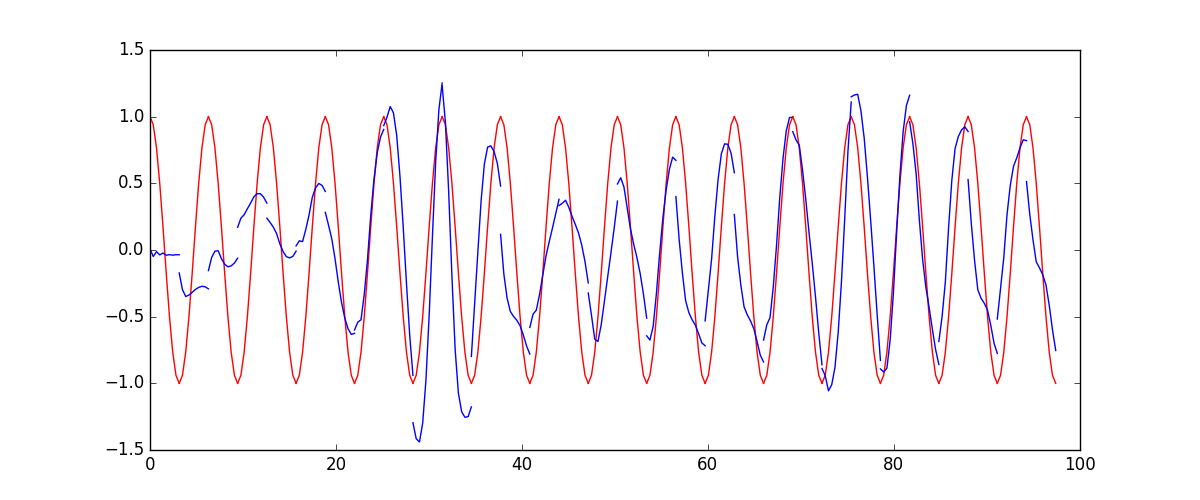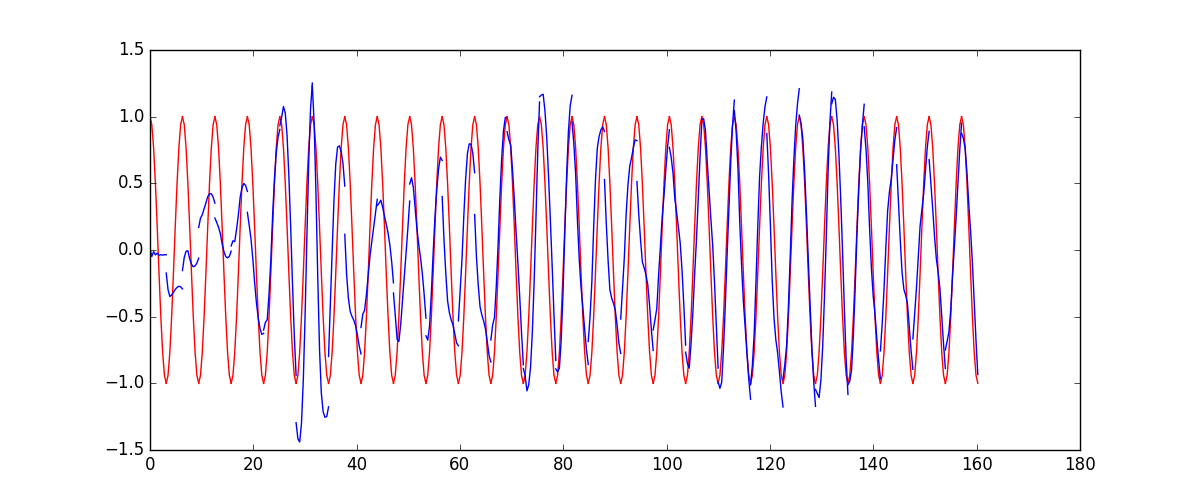
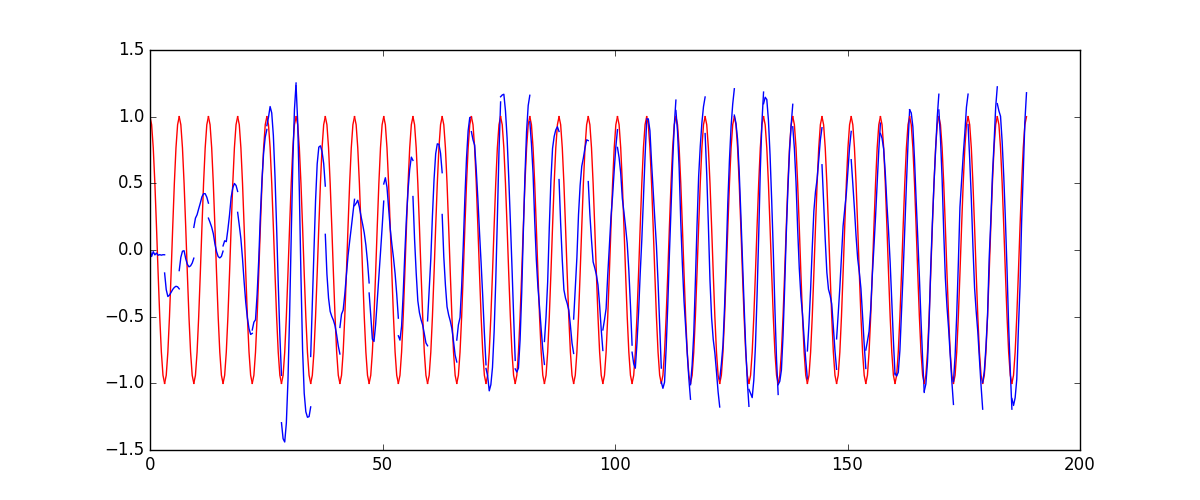
下面的代码就能实现动图的效果啦~开心, 可以看出, 我们使用 x 作为输入的 sin 值,
然后 y 作为想要拟合的输出, cos 值. 因为他们两条曲线是存在某种关系的, 所以我们就能用
sin 来预测 cos. rnn 会理解他们的关系, 并用里面的参数分析出来这个时刻 sin 曲线上的点如何对应上
cos 曲线上的点.
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all rnn parameters
loss_func = nn.MSELoss()
h_state = None # 要使用初始 hidden state, 可以设成 None
for step in range(100):
start, end = step * np.pi, (step+1)*np.pi # time steps
# sin 预测 cos
steps = np.linspace(start, end, 10, dtype=np.float32)
x_np = np.sin(steps) # float32 for converting torch FloatTensor
y_np = np.cos(steps)
x = torch.from_numpy(x_np[np.newaxis, :, np.newaxis]) # shape (batch, time_step, input_size)
y = torch.from_numpy(y_np[np.newaxis, :, np.newaxis])
prediction, h_state = rnn(x, h_state) # rnn 对于每个 step 的 prediction, 还有最后一个 step 的 h_state
# !! 下一步十分重要 !!
h_state = h_state.data # 要把 h_state 重新包装一下才能放入下一个 iteration, 不然会报错
loss = loss_func(prediction, y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
所以这也就是在我 github 代码 中的每一步的意义啦.
分享到:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
如果你觉得这篇文章或视频对你的学习很有帮助, 请你也分享它, 让它能再次帮助到更多的需要学习的人.
莫烦没有正式的经济来源, 如果你也想支持 莫烦Python 并看到更好的教学内容, 赞助他一点点, 作为鼓励他继续开源的动力.